Class-7 Science Chapter-9 Soil, Additional Exercises in line with NCERT book / CBSE Syllabus
Chapter 9
Soil
Exercises from
textbook
Additional
Exercises
Activities/Projects
Additional Exercises
Choose the correct answer:
(1) soil profile can be seen
a.
At
the sides of a road on a hill
b.
At
a steep river bank
c.
While
digging foundation of a building and a well
d.
All
the above (√)
(2) Which type of soil will be the best for
making pots, toys and statues?
a.
Sandy
soil
b.
Clayey
soil (√)
c.
Loamy
soil
d.
All
the above
(3) Which soil has the highest percolation
rate?
a.
sandy
soil
b.
clayey
soil (√)
c.
loamy
soil
d.
None
of the above
(4) Which soil has the lowest percolation
rate?
a.
Sandy
soil (√)
b.
silt
c.
clayey
soil
d.
loamy
soil
(5) Which of these climatic factor affects
the soil?
a.
Wind
and rainfall
b.
temperature
c.
light
and humidity
d.
All
the above (√)
(6) Which of these soils is suitable for
growing cereals like wheat and gram?
a.
Clayey
soil
b.
Loamy
soil
c.
Both
a and b (√)
d.
None
of these
(7) Which of these soils is suitable for
cotton?
a.
sandy-loam
b.
loam
c.
Both
a and b (√)
d.
Clayey
(8) Which of these soils is required for
lentils (masoor) and other pulses?
a.
loamy
soil (√)
b.
sandy
soil
c.
clayey
soil
d.
Any
of these
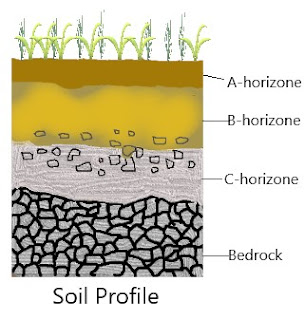
Match
the column:
|
A
|
B
|
|
A- horizon
|
This layer has lesser amount of humus but
more of minerals
|
|
B-horizone
|
This layer is hard and difficult to dig with
a spade
|
|
C-horizone
|
This layer is generally soft, porous and can
retain more water
|
|
Bedrock
|
This layer is made up of small lumps of
rocks with cracks and cervices
|
Ans
|
A
|
B
|
|
A- horizon
|
This layer is generally soft, porous and can
retain more water
|
|
B-horizone
|
This layer has lesser amount of humus but
more of minerals
|
|
C-horizone
|
This layer is made up of small lumps of
rocks with cracks and cervices
|
|
Bedrock
|
This layer is hard and difficult to dig with
a spade
|
State whether the following statements are True
or False:
1-
Soil is home for many organisms. (True)
2-
Use of agricultural pesticides does
not harm the soil. (False)
3-
The rotting dead matter in the soil
is called bedrock. (False)
4-
Silt occurs as a deposit in river
bed. (True)
Give one word for the following:
(1)
Narrow
opening in the rock. (Crevice)
(2) The soil which contains greater
proportion of big particles. (Sandy Soil)
(3) The soil which has relatively higher
proportion of fine particles. (Clayey soil)
(4) The soil which has about the same
promotion of large and fine particles. (Loamy soil)
Encircle the Odd one:
(1) Sandy soil, Silt, Loamy soil, Clayey soil (Type of soil)
(2) Humus, Bedrock, Silt, Plant roots. (Found in top
soil)
Fill in the blanks:
(1) The mixture of rock particles and humus is
called the soil.
(2) Clay soils are heavy as they hold more water.
(3) The size of silt particles is between
those of sand and clay.
(4) The rotting dead matter is called humus.
Answer the following
questions:
Q.
How is soil formed? What is this process called?
Ans- Soil is
formed by the breaking down of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate.
This process is
called weathering.
Q.
How is soil important?
Ans- Soil is
important in following ways:
1- It supplies
water and nutrients to plants.
2- It supports
the growth of plants by holding the roots firmly.
3- Soil is the
home for many organisms.
4- Soil is
essential for agriculture and agriculture provides food, clothing and shelter
to all.
Q.
Mention two factors on which the nature of soil depends.
Ans- The nature
of soil depend on-
1- The rocks
from which it has been formed.
2-
Type of vegetation that grows in it.
Q. What is silt?
Ans- Silt is a
type of soil particle. Silt occurs as a deposit in river beds. The size silt
particles is between those of sand and clay.
Q. Make a labelled diagram of various horizons in soil profile.
Q.
Which kind of soil would be most suitable for planting rice? Soil with a higher
percolation rate or soil with a low percolation rate?
Ans- Rice crop
needs more water; therefore, soil with low percolation rate is most suitable
for planting rice.
Q.
A certain sample of soil takes 20 minutes for 200 mL of water to percolate.
Calculate the rate of percolation in the soil sample.
Ans- Given
(1) Amount of water= 200 mL
(2) Percolation time= 20 min
(3) Rate of percolation=?
Rate
of percolation = amount of water (mL) / percolation time (mL)
Rate
of percolation = 200 mL/20 min = 10 mL/min
Q.
What type of soil is ideal for paddy?
Ans- For paddy,
soil rich in clay and organic matter and having good capacity to retain water
is ideal.
Q.
What is soil erosion? How is it connected with plants? Write some measures to prevent soil erosion?
Ans- The
removal of land surface by water, wind or ice is known as erosion. Plant roots
bind the soil firmly. In the absence of plants, soil becomes loose and it can
be moved by wind and flowing water.
Following are
some measures ti prevent soil erosion.
1- Cutting of
trees should be avoided.
2-
Deforestation should be minimized.
3- Make efforts
to increase the green cover on earth.
Q.
How does the soil get polluted? Mention some measures to prevent soil
pollution?
Ans- Soil gets polluted by mixing of a number of
waste products including municipal, industrial wastes, plastics, chemicals and
pesticides. Plastic and polythene bags not only pollute the soil but also kill
the organisms living in the soil.
Following are
some measures to prevent soil pollution:
1- Waste
products and chemicals should be treated before they are released into the
soil.
2- Use of
pesticides should be minimised.
3- Polythene
bags and plastics should be banned from throwing in garbage.
Give reason. Why?
Sandy
soil tends to be light, well aerated and rather dry.
Ans- Sand
particles present in the sandy soil are quite large. They cannot fit closely
together, so there are large spaces between them. These spaces are filled with
air so we say that it is well aerated. Water can drain quickly through the
spaces between the sand particles. So, the sandy soil tend to be light well
aerated and rather dry.
Clayey
soil is used to make pots, toys and statues.
Ans- Clayey
soil has clay particles which are much smaller and pack tightly together
leaving little space for air. This soil does not contain coarse particles, can
be moulded into various shapes and also becomes hard on drying. Therefore it is
used for making pots, toys and statues.
Loamy
soil is best for growing plants.
Ans- Loamy soil
is the best top soil for growing plants. This soil is a mixture of sand, clay
and silt. Loamy soil also has humus in it. It has the right water holding
capacity for the growth of plants.
The
air above a farmland during a hot summer day is shimmering.
Ans- On a hot
summer day, the vapour coming out of the soil reflect the sunlight and the air
above the soil seems to shimmer.
Wheat
are grown in fine clayey soil.
Ans- Wheat is
grown in fine clayey soil because they are rich in humus and are very fertile.
Exercises from Textbook
Pick
the most suitable answer in questions one and two
1-
In
addition to the rock particles, the soil contains
a.
Air
and water
b.
Water
and plants
c.
Minerals,
organic matter, air and water(√)
d.
Water,
hair and plans
2-
The
water holding capacity is the highest in
a.
Sandy
soil
b.
clayey
soil (√)
c.
loamy
soil
d.
mixture
of sand and loam
Match
the items in column 1 with those in column 2
|
Column 1
|
Column 2
|
|
A home for living
organisms
|
Large particles
|
|
Upper layer of the soil
|
All kinds of soil
|
|
Sandy soil
|
Dark in colour
|
|
Middle layer of the soil
|
Small particles and packed tight
|
|
Clayey soil
|
Lesser amount of humus
|
Ans-
|
Column 1
|
Column 2
|
|
A home for living
organism
|
All kinds of soil
|
|
Upper layer of the soil
|
Dark in colour
|
|
Sandy Soil
|
Large particles
|
|
Middle layer of the soil
|
Lesser amount of humus
|
|
Clayey soil
|
Small particles and packed tight
|
Q.
Explain how soil is formed?
Ans- Soil is formed by the breaking down
of rocks by the action of wind, water and climate.
This process is called weathering. It is
made up mainly of mineral particles, organic materials, air, water and living
organisms—all of which interact slowly yet constantly. Most living beings on
earth depend on the soil for their existence.
Q.
How is clayey soil useful for crops?
Ans- Clayey soil is useful for crops in following
ways:
1-
It's particles are fine and tightly packed, so it has good water retention
capacity.
2-
This soil has low percolation rate.
3-
It is rich in humus, so it is very fertile.
Q.
List of the differences between clayey soil and sandy soil
Ans-
|
Clayey
soil
|
Sandy
soil
|
|
The proportion of fine
particles is high in clayey soil.
|
Proportion of big
particles is higher in sandy soil.
|
|
It has very good water
holding capacity.
|
It has poor water
holding capacity.
|
|
This soil is very
fertile.
|
It is not fertile.
|
|
It has low percolation
rate.
|
It has high percolation rate.
|
|
It's particles are
tightly packed.
|
It's particles are loosely packed.
|
|
Air content is low.
|
Air gets trapped in the soil.
|
|
Suitable for crops.
|
Not suitable for crops.
|
Q.
Sketch the cross section of soil and label the various layers.
Ans-
Q.
Razia conducted an experiment in the field related to the rate of percolation.
She observed that it took 40 minutes for 200 ml of water to percolate through
the soil sample. Calculator rate of percolation.
Ans- Given
(1) Amount of water-cooled 200 mL
(2) Percolation time = 40 min
(3) Percolation rate=?
Percolation
rate (mL/min) = amount of water (mL)
percolation
time (min)
= 200 mL / 40 min
= 5 mL/min
Q.
Explain how soil pollution and soil erosion could be prevented.
Ans- Following
are some measures to prevent soil pollution:
1-
Bane
throwing to plastic waste in soil and minimize its use.
2-
Use bio-pesticides and bio-insecticides instead
of chemical pesticides and insecticides.
3-
Use
manure and vermi-compost instead of chemical fertilizers.
4-
Treat
industrial waste wasted before mixing it in soil.
5-
Plant
more trees.
Following are
the measures to prevent soil erosion.
1-
Reduce
deforestation for urbanization and industrialization.
2-
Planting
more trees along the sides of roads.
3-
Regenerate
forests with people involvement.
4-
Plant
grass and shrubs in open fields.
5-
Make
effective drainage system to prevent top soil from being washed away.
Solve
the following crossword puzzle with the clues given:
|
1W
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
I
|
|
2E
|
R
|
O
|
S
|
I
|
O
|
N
|
|
|
|
|
|
N
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
3 W
|
|
|
|
D
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H
|
|
|
|
|
|
4S
|
|
5P
|
R
|
O
|
F
|
I
|
L
|
E
|
|
|
|
|
|
A
|
|
O
|
|
|
|
|
|
A
|
|
|
|
|
|
N
|
|
L
|
|
|
|
|
|
T
|
|
|
|
|
|
D
|
|
Y
|
|
6C
|
L
|
A
|
y
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
Y
|
|
T
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
H
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
E
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
N
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
|
7E
|
A
|
R
|
T
|
H
|
W
|
O
|
R
|
M
|
Across
(2
)Plantation prevents it.
(5)
Use should be banned to avoid soil pollution.
(6)Type
of soil used for making pottery.
(
7)Living organisms in soil.
Down
(
1) In desert soil erosion occurs through.
(
3)Clay and loan are suitable for cereals like.
(
4) This type of soil can hold very little water.
(
5) Collective name for layers of soil.
Extended learning - activities and projects
1-
Boojho
you would like to know the difference between raw and baked soil. Investigate
how the soil from the matkas are different from the soil used to make statues.
2-
Paheli
is worried. She could see a brick kiln from her house. Bricks were being made
there. There was so much smoke coming out of the kiln. She was told that the
best quality of clay is required for making pottery, statues and bricks. She
has seen truckloads of bricks being taken away for construction of buildings.
At this rate, she fears, no soil will be left. Are her fears justified? discuss
this problem with your parents, teachers and other experts of your area and
prepare a report.
3-
Try
to find the moisture content of a soil sample. One method is given here.
Activity-
Take 100g soil. (Take help from any shopkeeper to weigh the soil.) place it on
a newspaper in the Sun and allow it to dry for two hours. This activity is best
done in the afternoon. After drying it, weigh the soil again. The difference in
the vet of the soil before and after drank gives you the amount of moisture
contained in hundred gram of side. This is called the percentage moisture
content.
Suppose
your sample of story loses hundred gram
on drying. Then
Per
cent of moisture in soil = Wt. of
moisture (g) × 100
Original wt. of soil sample (g)
In
this example
Per
cent of moisture in soil = 10 × 100 / 100 = 10%
|
Did you know?
|
|
Rivers of north India,
which flow from Himalayas, bring a variety of materials including silt, clay,
sand and gravel. They deposit their materials called alluvial soil, in the
planes of north India. This soil is very fertile and supports nearby half the
population of India.
|




Comments
Post a Comment